Overland Tech and Travel
Advice from the world's
most experienced overlanders
tests, reviews, opinion, and more
The new Defender appears, sort of . . .
Currently making the rounds of forums, at last, is a photo of a heavily disguised test prototype of the much-awaited, much-delayed, resurrected and re-invented Land Rover Defender.
The speculation about this vehicle has been on a level like nothing I’ve seen in the four-wheel-drive universe, even beyond the theories that swirled around Jeep’s re-designed Wrangler.
The Wrangler rumor mill terrified aficionados with hints that the new model would lose its solid front axle for independent suspension—perhaps even on the rear axle as well. Then we heard its separate, fully boxed chassis would be abandoned for unibody construction, rendering it in the faithful’s eyes no more than a glorified jacked-up sedan.
In the event, the new JL Wrangler stayed built the way God intended Jeeps to be built: solid front and rear axles, body-on-fully-boxed-frame construction. Parent company FCA managed to incorporate modern safety and convenience features into a decades-old blueprint, and the new Wrangler remains a superb choice for extended travel in rough country.
Tragically, at least for thousands of traditionalist Land Rover faithful, the exact same rumors (or perhaps I should say rumours) proved well-founded as Jaguar/Land Rover gradually released details of the new Defender. The 2020 replacement for the 70-year-old expedition icon will ride on all-independent suspension and will be built on aluminum-intensive unibody architecture shared with other Jaguar/Land Rover products.
Thus one thing is clear: The old Defender is dead and buried (recent outrageous £150,000 factory specials notwithstanding). No more will Land Rover ship CKD (Complete Knock Down) Defenders in crates to be assembled in developing-world countries and pressed into rough service in the remotest backwaters of the Realm. No more will adventurous owners boast of accomplishing major drivetrain rebuilds with hand tools outside an Angolan village. The new Defender will be a completely different vehicle than the old one. The question is, will it be a better vehicle?
J/LR swears the new Defender will be more capable off-road than its predecessor—not at all an outrageous claim given the huge advancements in traction control systems since the relatively primitive system installed in the last generation. And, honestly, it won’t be difficult to exceed the capabilities of the pre-traction-control Defenders, which relied solely on gearing and compliant suspension to negotiate challenging terrain, thanks to Land Rover’s obstinate decades-long refusal to fit cross-axle differential locks. Even the independent suspension will only be a handicap in certain situations, such as when both front wheels compress upon hitting an obstacle, reducing clearance to the fixed front differential. It will certainly enhance ride and handling. And while traditionalists might not like it, unibody construction actually results in a vehicle with far higher torsional rigidity than a vehicle riding on a separate frame, even a fully boxed one. You simply lose the ability to unbolt the body from the chassis with your sockets and wrenches. And repairing collision or trail damage on a unibody vehicle is considerably more involved.
So the capability will be there. Whether J/LR offers the new Defender in suitably basic form to satisfy those who eschew leather and carpet and 10-inch entertainment screens in their overland vehicles—as well as to create an affordable version—remains to be seen.
One area where I suspect the company will get it right is styling—not that there’s much to tell from the disguised test vehicle. After the PR disaster that was the DC100, I’m willing to bet J/LR went to great lengths to evoke the original’s styling without being overtly retro. I predict it will look properly sturdy and adventurous.
Thus we’ll have a capable vehicle that looks the part. The only remaining big question involves market placement. Will Jaguar/Land Rover aim for existing Defender owners, or will they exploit that iconic model name and shove it toward the upscale end of buyers, those who want the look and the rugged association, but who wouldn’t dream of actually shipping their rugged-looking vehicle around the Darien Gap or across the Strait of Gibraltar and exploring another continent?
If you look at sales history I think the answer is clear. The last Defender—the solid-axle, separate frame, bolted-together genuine expedition machine, went extinct for one reason: It stopped selling. Why would Land Rover aim at the exact same customers with the new one?
In some ways the decision will be out of their hands. A technologically advanced vehicle, built largely out of aluminum, with all-independent suspension, sophisticated traction-control and safety systems, and advanced powerplants, is going to be expensive to produce and will cost a lot to buy. I’ll wager the base price of the new Defender 110 (or whatever it will be called) will be substantially above that of the already dear Wrangler Rubicon Unlimited. The temptation to just go with that and load it up with leather and carpet and entertainment screens will be powerful.
I’ll wager further that ads for the new Defender will be stoked with historical family references, and heavy on images in rainforests and sand dunes. Just which magazines those ads appear in will betray the direction the new Defender will take—towards the real jungle or the concrete one.
The versatile 1/4-inch ratchet . . .
The ratchet and socket set is the most critical component of your tool kit. It’s what comes out when things need attention that are held on to the vehicle with actual nuts and bolts, rather than just trim screws or plastic press fittings. Important things, in other words. I’ve always maintained it’s the part of your kit you should spend the most money on, to get the absolute highest quality. Of all the tools I’ve broken over the years, the majority by far have been cheap sockets that split, or cheap ratchets that jammed or broke altogether.
Most owners—me included—start out with a 3/8ths-inch ratchet and socket set (the 3/8ths refers to the diameter of the anvil, the square peg on the ratchet to which you attach the sockets). A 3/8ths set will comfortably handle bolts or nuts from about 9mm or 5/16ths inch up to 19mm or 3/4 inch. That’s suited for a lot of medium-sized repairs—replacing fan or serpentine belts, water pumps, radiators, etc. Above that you really should step up to a 1/2-inch ratchet, which is able to handle larger sockets for fittings such as those on suspension components, which need more torque to remove or fasten securely.
Thus for a long time my automotive tool kit has included a 3/8ths-inch ratchet and socket set for general work and a 1/2-inch set for major repairs. And that worked just fine. But lately I’ve been rethinking. Why? Several reasons.
Even a 3/8ths ratchet can be a bit long and bulky when working in tight spaces on fasteners smaller than 11 or 12mm. Yes, you can add a short-handled ratchet to the kit, but the head will still be just as bulky. And your 3/8ths socket set will probably have a lot of overlap with your 1/2-inch set. Typically the former will include sockets up to about 19mm, and the latter will include sockets down to 12mm. I’d rather use a 1/2-inch ratchet for that 19mm nut, yet a 1/2-inch ratchet is silly overkill for any 12mm bolt or nut I’ve ever encountered.
Enter the 1/4-inch ratchet. It’s smaller all around, able to fit into spaces no 3/8ths equivalent could. You can argue that the ratcheting mechanism is inevitably weaker as well, but consider two things: First, there is only so much torque necessary for even a 12 or 13mm fastener; second, a high-quality ratchet will withstand force comfortably in excess of any you’re likely to need. I’ve yet to meet a 12mm or even 13mm nut that I couldn’t remove with a 1/4-inch ratchet. And it will be far handier for smaller sizes.
Additionally, a 1/4-inch ratchet and socket set will cost less than a larger one, so you can go for higher quality. Finally, the 1/4-inch set will be lighter and take up less space, a surprisingly real consideration even in something such as our Troop Carrier, the tool bin of which is approaching maximum capacity and the GVWR of which is approaching, period.
So I’ve been wondering if a versatile combination might be a 1/4-inch set with sockets ranging from very small, say 4 or 5mm, up to about 13mm, and a 1/2-inch set with sockets from 12 or 13mm up to whatever you like—my current set goes up to 32mm. The slight overlap would mean that if you ever did run into a recalcitrant 12 or 13mm bolt while using the 1/4-inch kit, you could switch up to the 1/2-inch.
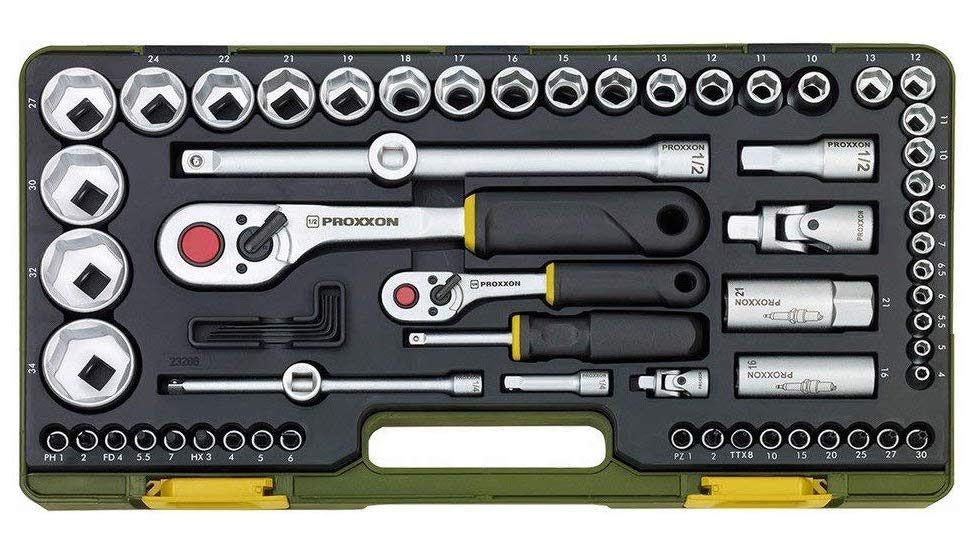
I have a nice mixed set of 1/4-inch stuff, but this scheme was a perfect opportunity to spend money on tools. I like investigating brands new to me, and my friend, driving trainer extraordinaire Graham Jackson, is fond of the German brand Proxxon, so I looked them up on Amazon, and ordered the 23280 49-piece “Precision Engineer’s” 1/4-inch drive set.
The first thing that impresssed me was the box it came in. While plastic rather than metal, it had decent sliding latches rather than the usual flimsy snap latches with stressed-plastic hinges, which invariably fail. A nice touch.
Inside I first examined the ratchet itself. The mechanism was a fine 72-tooth unit. Check. Push-button release, check. Lever-operated reversing switch, check. Perfect. The offset head is supposed to ease access to tight spaces. Not sure about that one.
The selection of sockets was very good. Standard sockets from 4mm to 13mm—perfect. They’re forged from chrome vanadium with a double-nickel and single chrome layer finish for corrosion resistance. They of course employ a copy of Snap-on’s Flank Drive system to help grip rounded off nuts (and to avoid rounding them off). A bonus was a comprehensive selection of bits for either the ratchet or the included driver: Screwdriver bits, hex bits, and Torx bits. Five sockets for external Torx fittings. There was even a little selection of angled allen keys, 1.25 to 3mm. The set included two ratchet extensions—one of which included a (removable) sliding T-bar fitting—and a universal joint.
The only flaw I found was the paucity of deep sockets—just four of them, in 6, 7, 8, and 10mm. Odd. Why not a full complement up to 13mm? I would have traded the external Torx sockets for them. As it was there was no space in the tray for additional sockets. But . . . what’s this? There appeared to be some voids in the box under the molded tray. Indeed, when I lifted it out there were several generous gaps.
I called the U.S. Proxxon headquarters. They told me they don’t directly import the hand tools sets, only power tools (I bought mine through a third party dealer). However, when I told them what I was trying to do they generously offered to special-order the sockets I wanted. So I filled in the deep sockets and bought a flexible drive extension as well. All those plus a Snap-on flex-head 1/4-inch ratchet fit underneath the tray.
I guess I need to clean up those holes.
Now I had a comprehensive 1/4-inch socket and ratchet set with the bonus of the driver bits and handle. As expected, it was significantly more compact than an equivalent in 3/8ths. The last task was to make it easier to get the molded tray out when I wanted the stuff in the bottom. So I Dremelled two slots in the tray, and ran a piece of flat 1/2-inch webbing through them and under the tray, leaving the ends loose on top. It’s now easy to pull the tray free.
Our Troop Carrier has a comprehensive set of tools, but they live in a cabinet under a bench that is somewhat of a pain to get to. I’ve been wanting to have a more convenient tool kit for small repairs and adjustments. This Proxxon set, with its combination of sockets and bits, should fill that role perfectly—and it’s compact enough to fit behind a seat.
Hmm . . . I wonder if I should order another two or three sets?
Epilogue: Regarding my idea that a 1/4-inch socket set combined with a 1/2-inch set might be all one needs for just about any job: Proxxon sells a kit (23286) that combines just that, with sockets from 4mm all the way to 34mm. Impressive. Just add some deep sockets and a breaker bar.
When equipment makers go under
Recently the overlanding forums have been buzzing—steaming might be a better verb—with the news of a bankrupcty filing by a (formerly) respected maker of aftermarket bumpers and skid plates—and the concomitant loss of the deposits of a good number of innocent customers.
Similar sagas have followed an all-too-common pattern. A company with a solid reputation for quality overextends itself with the orders flowing in after many positive reviews from journalists and previous owners. First it can’t keep up with production, and deliveries fall behind. Zealous overspending early on—a bigger factory, a new truck (or house) for the owner—now means that incoming deposits are used to purchase materials for products that were ordered months before. Cash runs short, then out altogether. By the time enough customers realize what’s happening and post warnings on relevant forums, dozens of later customers are already out of luck as well. And throughout it all the company’s website stays active, inviting the unaware to click “Buy now,” in a desperate bid to get more cash to try to catch up with a cascading backlog of production.
This has happened before in my experience with companies servicing the overlanding market—once with a maker of top-of-the-line bumpers and roll cages for Land Rovers and Ford trucks, once with a very high-profile manufacturer of luxury truck-based campers. Given the exploding popularity of overland travel and the associated equipment (and the Great Recession that hit just as the activity was gaining traction), I’m surprised it hasn’t happened more frequently—businesses go out of business while making money all the time, due to other factors that can range from poor management to the management snorting the profits or letting it ride on 32 red.
The reasons are of little concern to those who have lost hundreds or thousands of dollars after placing a deposit or even paying in full for a product they have every expectation of receiving in a reasonable amount of time.
What can a consumer do? In most cases, thorough prior research into the company’s reputation will suffice, especially if you look up current forum posts regarding their products and customer service. Don’t look at only one thread or jump to conclusions from one post—just as there are customers with legitimate complaints, so are there trolls whose mission in life is to complain and badmouth in an attempt to make others as unhappy with life as they are.
Once you’ve committed to ordering a specific product, basic steps to protect yourself should be mandatory. Be sure all your correspondence with the company is in writing (email is fine), including specifications, final price, and, above all, a final delivery date. Consider negotiating a discount if delivery is late.
However, despite precautions there is always the chance you’ll be caught at just the wrong time, after trouble starts but before it becomes widely known. The next best defense is to use a credit card with a strong buyer-protection plan for any deposit you are required to put down. We once paid several thousand dollars to a service company that utterly failed in its promises to us. Fortunately we had used an American Express card, and when we provided complete documentation of the issues and our attempts to rectify them, we received a full credit from Amex.
Without a guaranteed way to recoup your money from your end, your chances of doing so from the company can be slim. If there are bankruptcy proceedings in court, you can bet the banks, steel suppliers, and landlords will get their claims way higher on the list than your piddly little $1,000 deposit.
Thankfully such situations are rare. But it’s always smart to practice due diligence.
The new ARB hydraulic Jack
It’s been a century and a decade since the Automatic Combination Tool, as the Hi-Lift jack was originally known, was introduced by Philip John Harrah, founder of Bloomfield Manufacturing. And for that 110-plus years, nothing else has achieved the versatility and capability of the Hi-Lift. It will raise two and a quarter tons anywhere from 22 to 46 inches in one continuous operation, depending on the model selected (36, 42, 48, or 60-inch). It can be used as a clamp, a spreader, and a winch. Its various parts have been employed as bodge fixes on countless broken vehicles—I used the tubular handle of one to sleeve a broken tie rod and get an International Scout back to civilization.
However. For all its strengths, the Hi-Lift has some significant issues. The most salient among them is that, if used carelessly, it has the capability to break any number of body parts on that user, from fingers to jawbones to skulls. When the operating lever is under tension (either lifting or lowering) it is extremely unwise—let’s just say stupid—to stray into the arc between it and the main beam. The Hi-Lift is heavy at 30 pounds for the popular 48-inch model. Finally, it is prone to jamming when exposed to road dirt, although a quick dousing with any spray lubricant will usually clear it.
And yet, surprisingly few attempts have been made to improve on the Hi-Lift (the raft of outright copies don’t count, of course). One attempt I tested about seven years ago (here), the Radflo Hydra-Jac, showed promise, since it operated hydraulically and there was no risk of kickback on the reassuringly small operating handle. And the Hydra-Jac weighed just 13 pounds. However, its lifting range was a relatively modest 18 inches, the round base was far too small, and, much more importantly, the jack’s capacity was a measly 2,200 pounds. It would barely get the front of my FJ40 off the ground; our Ford F350 would have laughed at it.
Enter the brand-new ARB JACK. That’s right, simply “jack” in all-caps. I hope no one got paid to come up with that. But let’s forgive them for the moment and look at the product. Note, however, that I will refer to the product as the ARB Jack, just one capital, because as a writer and grammarian I refuse to empower this lamentable trend toward all-cap product names (MAXTRAX, GLOCK, etc. etc.). You know those annoying people who post in forums in all-caps so it sounds like they’re YELLING AT YOU? That’s how I feel about all-cap product names.
Where was I? Right:
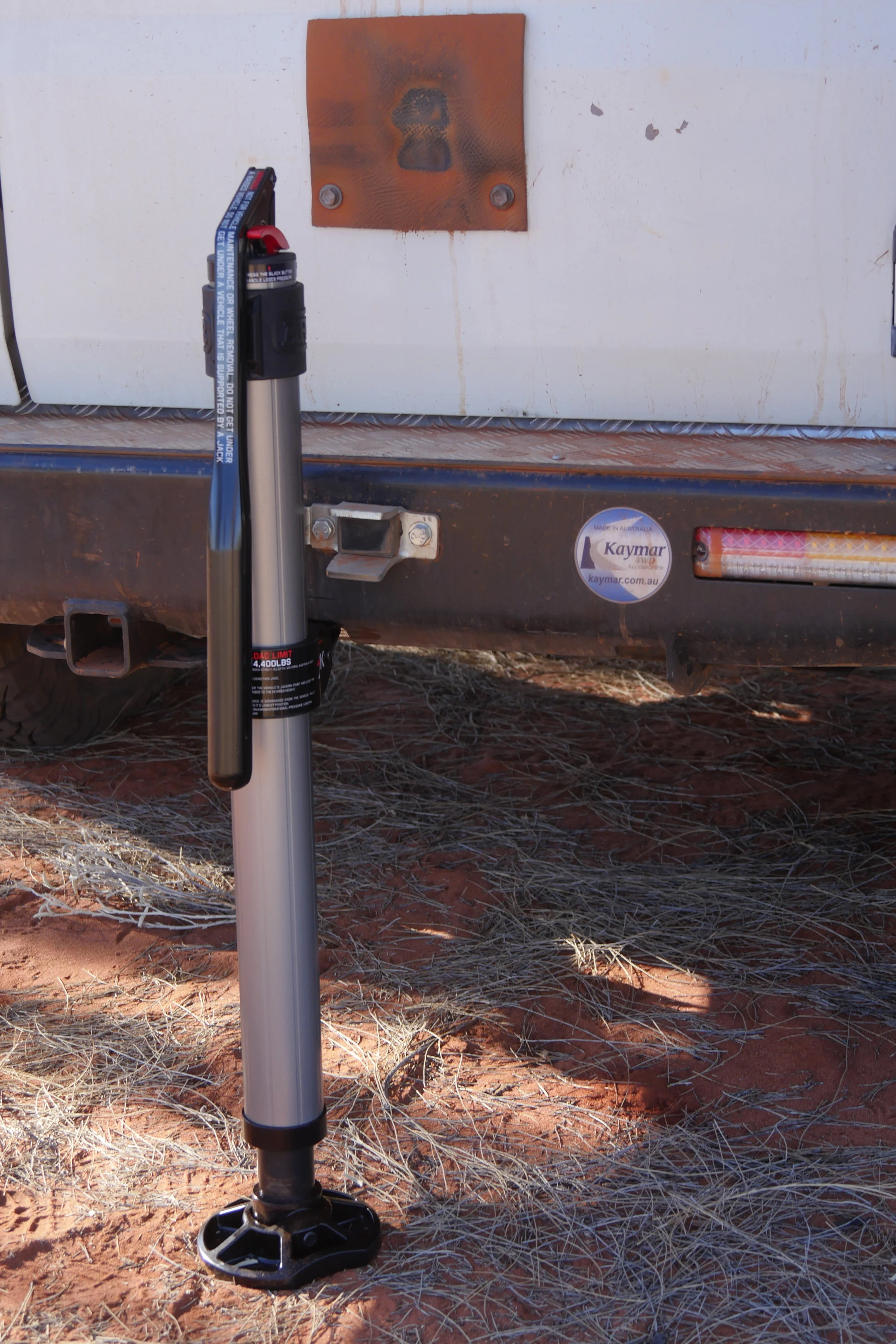
Like the Hydra-Jac, the ARB Jack is hydraulically operated. Distinctly unlike the Hydra-Jac, the ARB is rated to lift a proper, Hi-Lift-like 2,000 kilograms (4,400 pounds, and tested to 7,000). Furthermore, it will lift that 2,000 kg a full 48 inches off the ground. That’s 10 inches more than a 48-inch Hi-Lift. Yet when compressed the ARB is just 36 inches long. In its heavy-duty case our test sample fit easily crosswise behind the seats of our Troopy with room to spare. Impressive.
If that’s not enough to convince you this jack is a contender against the long-reigning heavyweight champion, note that the ARB Jack weighs just 23 pounds, a useful 25-percent reduction. Also, the handle of the ARB is not prone to flopping loose as the Hi-Lift’s handle will if you don’t have one of those polyurethane keeps slid over it. Combined with the short compressed length, this makes the ARB far easier to handle than a 48-inch Hi-Lift.
Last bit of empirical information: The ARB Jack can lift in precise 1/2-inch increments, unlike the larger jumps necessitated by the Hi-Lift’s climbing pins. And the ARB’s lowering lever (which takes a one-finger press to operate) has two speeds, so gentle or swift dropping is your choice. Literally effortless compared to lowering with a Hi-Lift (which is actually its most fraught procedure since if control is lost on the operating lever it can slam up and down in a violent feedback loop).
So far this sounds like a nearly complete shutout for the ARB Jack versus the Hi-Lift. But—we might as well get this over with now—there is an 800-pound gorilla in the room. Or, to be precise, an 812-pound gorilla, because the U.S. list price of the ARB Jack is $812. For that much cash you could buy yourself and seven friends a 48-inch all-cast Hi-Lift.
Is the ARB Jack worth it? After trying it out briefly on a trip through Australia, I’d say it depends on you. If you own a Hi-Lift that never comes off the roof rack or that pedestrian-mangler mount on the front bull bar, then you’d just be showing off to switch to the ARB. And I doubt many people will be mounting such a thief magnet to the outside of the vehicle anyway.
On the other hand, if your Hi-Lift is rusty, its red paint nearly gone, its jam-prone mechanism lubed over the years by everything from WD-40 to beer; if you’ve forgotten how many times it’s extracted your vehicle or that of a complete stranger, if it’s caught you out and smashed a finger or bruised a hand or worse, and if every time you use it you treat it like a capable and strong pack mule that hates your guts and is just waiting for a chance to kick your head in, then you might find the ARB Jack to be a bargain.
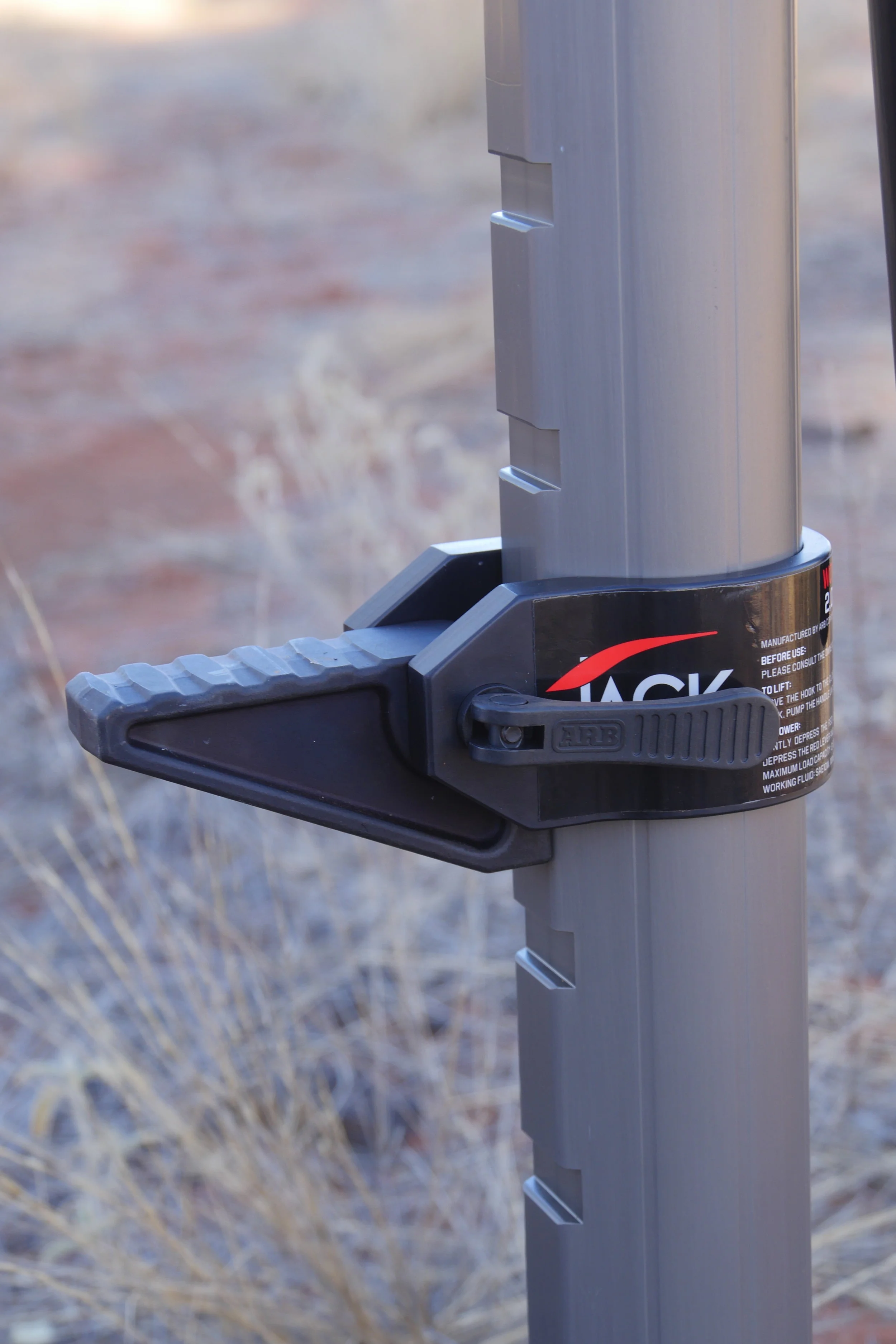
Nine slots facilitate easy adjustment of the tongue height.
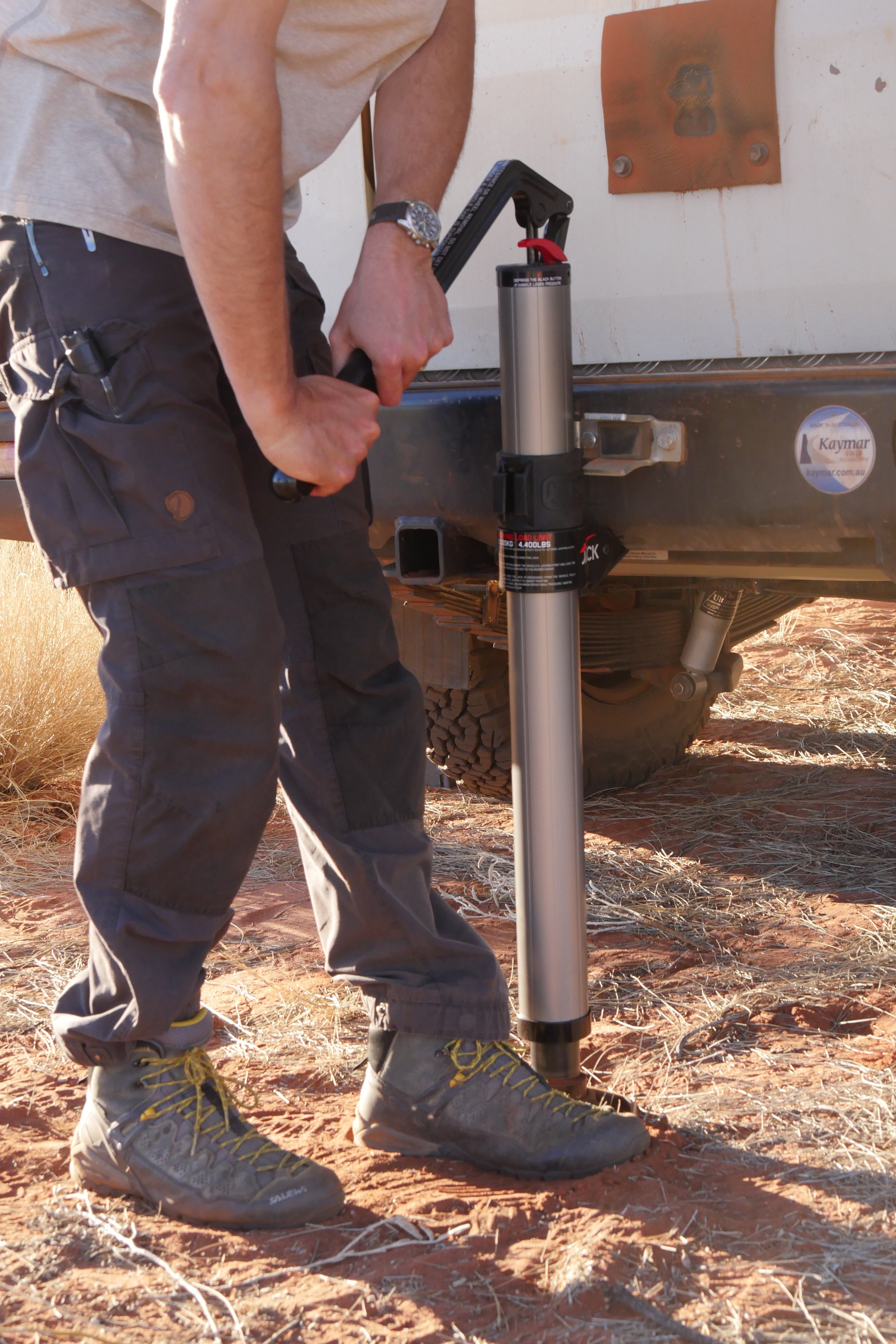
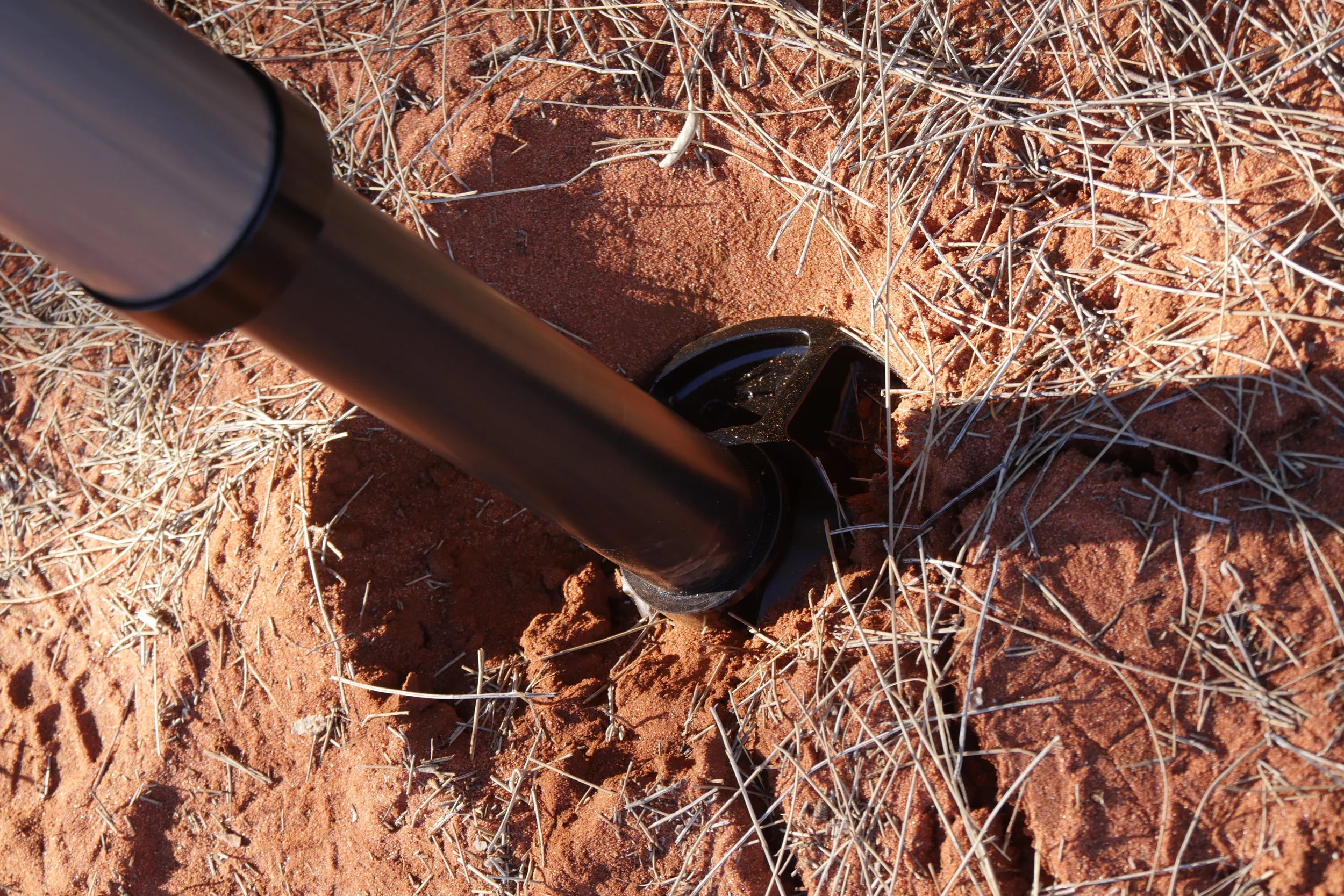
I used the Jack to raise the rear end of our Land Cruiser Troopy (via the dedicated jack slot in its Kaymar bumper, which the jack’s tongue fit perfectly), and immediately noticed the first advantage of the ARB over a Hi-Lift. When you lift the tongue of a Hi-Lift to fit into a bumper, you’re reducing its total lifting capacity by the height of the bumper. Not so the ARB Jack. Instead, the tongue itself slides up the jack and engages one of nine slots in the anodized aluminum alloy body, leaving the full lift capacity intact. Thus, although the total lift distance of the ARB is less than that of a 48-inch Hi-Lift, it will raise the vehicle higher. Only when lifting something from ground level will the Hi-Lift better it.
Only 36 inches tall stored, the ARB Jack will lift to a full 48 inches.
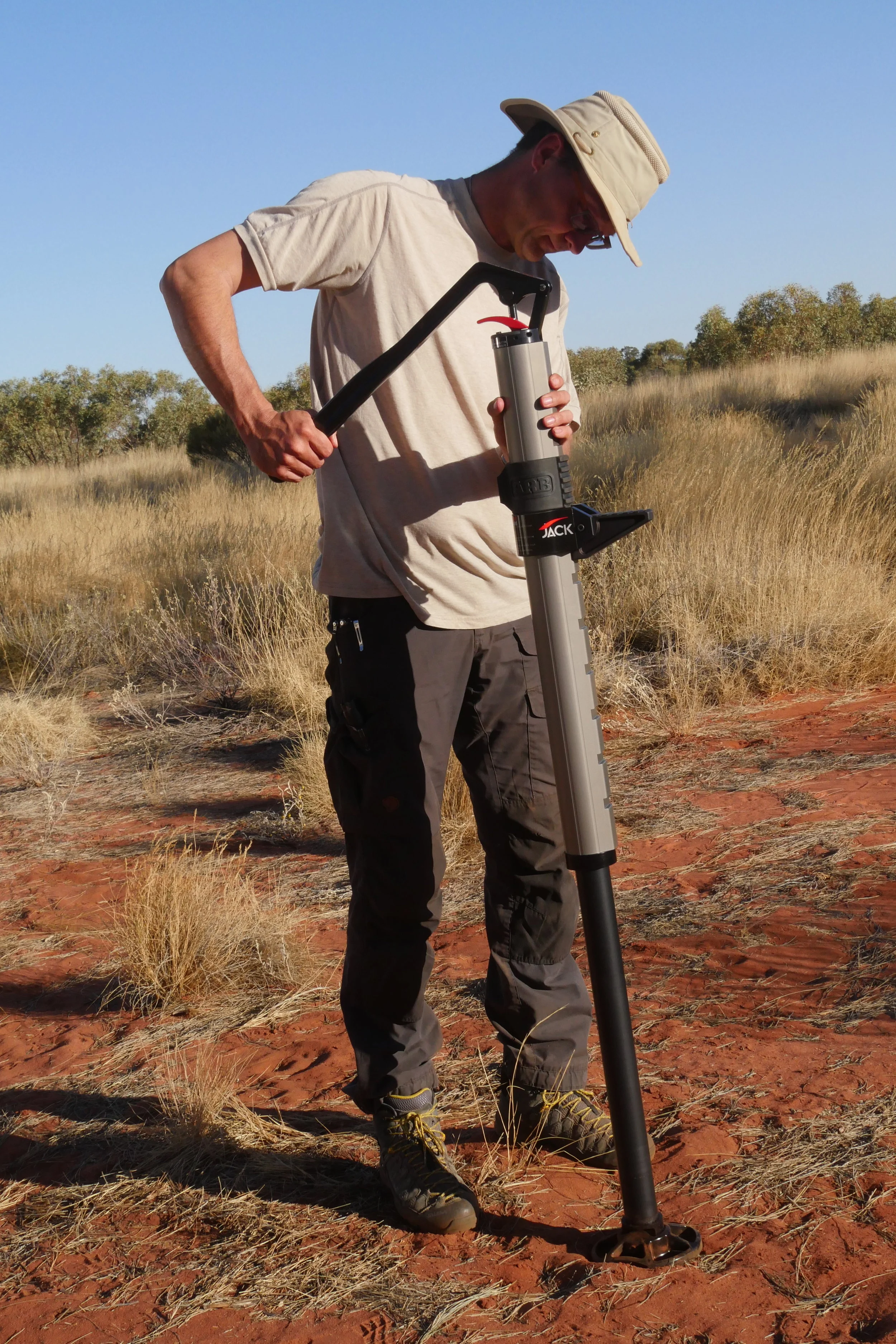
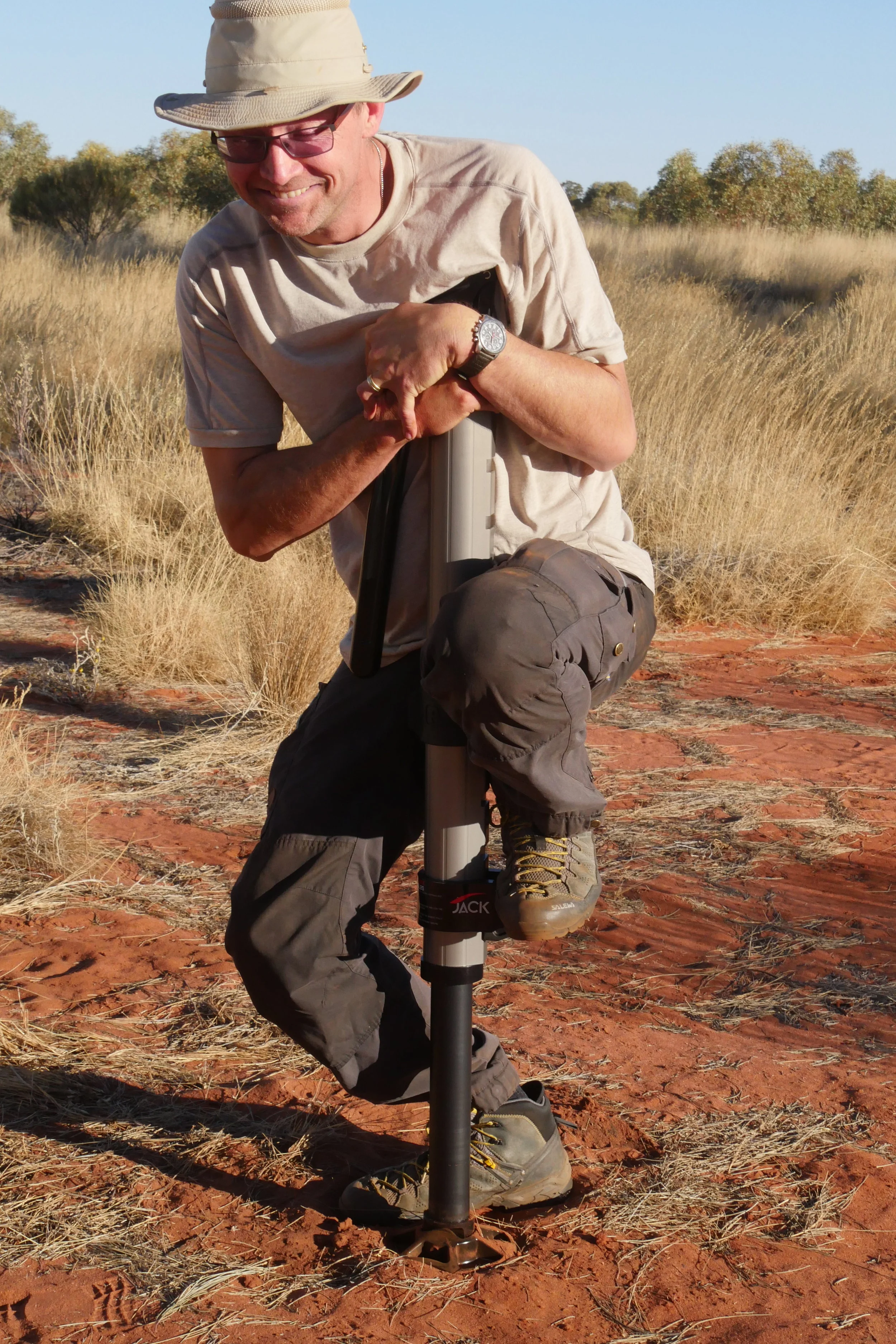
The next thing I noticed was expected, but still revelatory: Pumping the actuating handle is way, way easier than operating the lifting handle of a Hi-Lift. It’s much shorter and thus cannot exert the same leverage—but it doesn’t need as much leverage because the magic of hydraulics is doing much of the work for you. The back end of our Troopy is not exactly light—in addition to our pop-top camper unit, fridge, and cabinetry we have a 90-liter water tank and a Long Ranger 180-liter fuel tank closely tucked around the rear axle—but the back came up with remarkably little effort. I’ve taught Hi-Lift technique to a lot of people, and those under 140 pounds or so—men or women—often have trouble raising a very heavy vehicle, even with proper technique. They’ll have no such trouble with the ARB.
The short lifting handle is easy to operate, with zero chance of kickback.
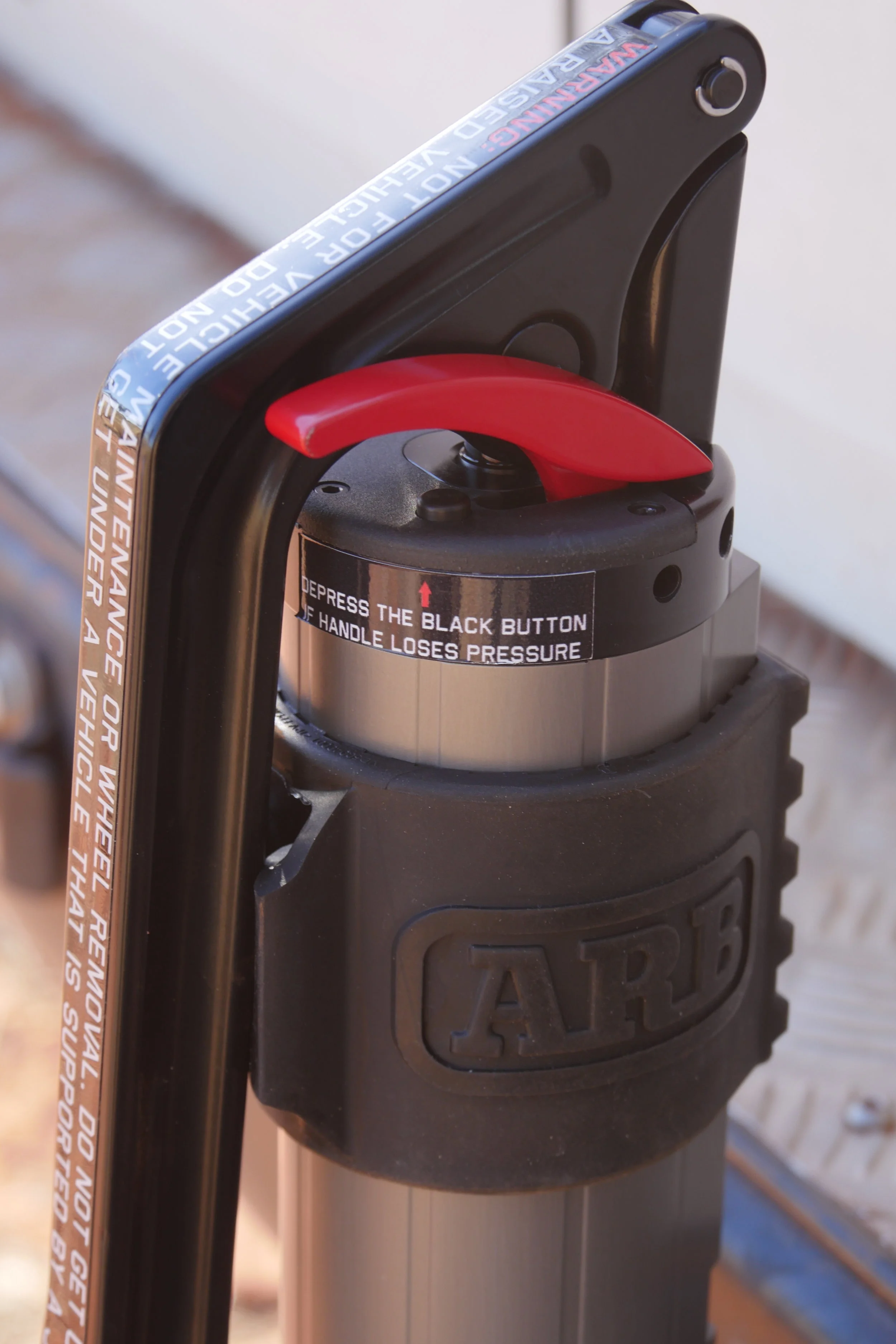
To lower, simply press the red lever.
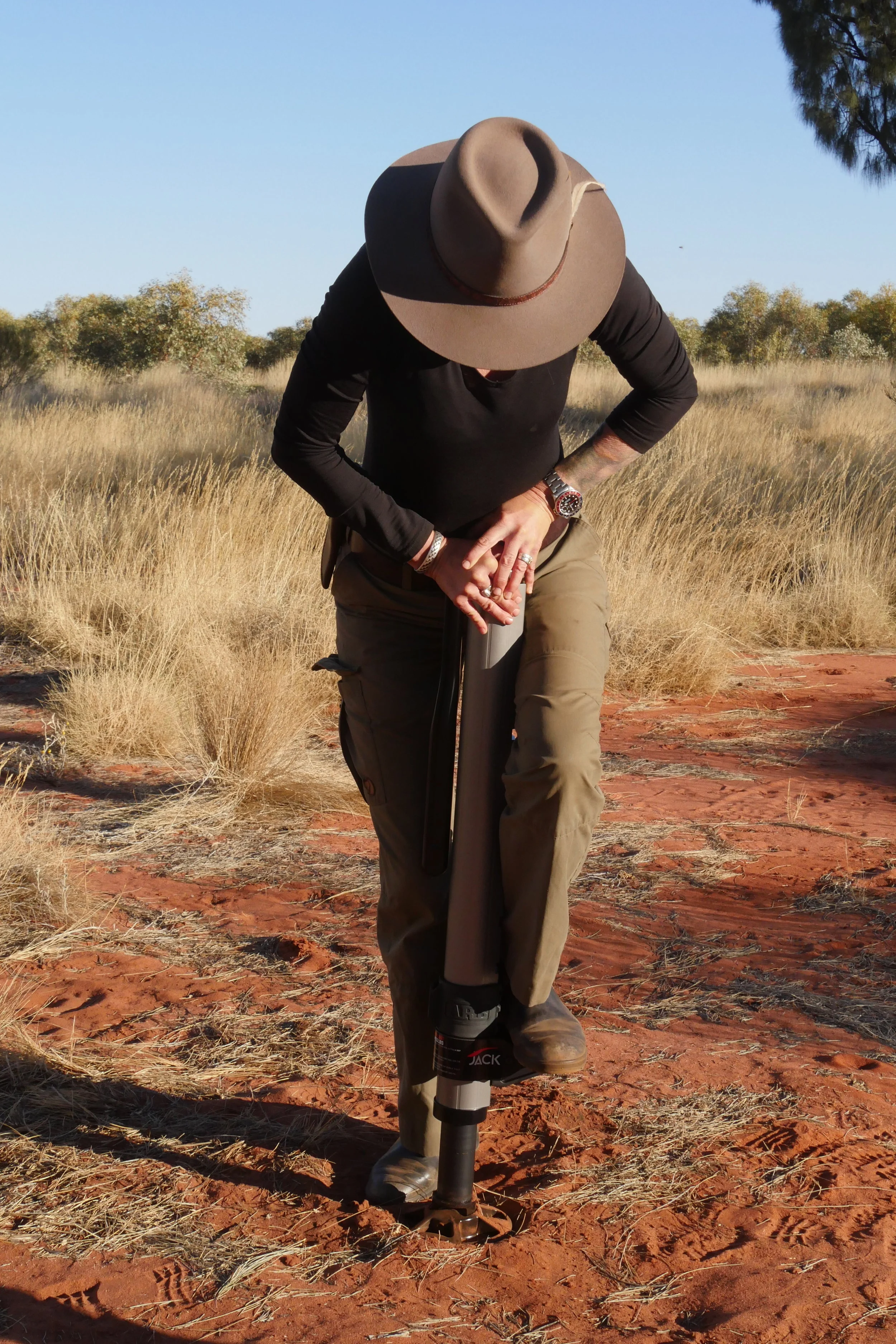
As for lowering—oh my is it easy. Lowering a weight with a Hi-Lift requires exerting exactly the same force one used to raise it, with the added risk of that feedback loop if one loses grip on the handle. Not possible with the ARB. Just press the little red lever with one finger, and down it goes, slow or fast, your choice; all at once or a half-inch at a time, your choice. Brilliant.
A heavy-duty ball joint allows the base to tilt about ten degrees.
Another aspect of the ARB revealed itself in the red sand of Australia’s Great Victoria Desert. Its mostly round base has more area than the rectangle of a Hi-Lift (34 versus 28 square inches), but it will still sink in soft substrate. Attempting to raise the Land Cruiser in sand resulted in more downward movement of the base than upward movement of the vehicle. And that round base does not fit in the rectangular receptacle of the standard red plastic jack base. I expect someone will quickly rectify this issue; in the meantime it would be easy to fab up your own from three layers of 3/4” plywood, with a cutout in the top layer to secure the base from sliding.
One characteristic of the ARB Jack did prove to be a bit of a pain. When you lower a Hi-Lift and the load on the tongue is relieved, the tongue and lifting assembly automatically drop free. With the ARB, once the load is off there is still considerable hydraulic resistance in the piston; lowering fully requires keeping the red lever pushed all the way down while leaning on the jack with enthusiasm—and it won’t happen quickly. I think a significant upgrade to this tool down the road would be a switch that engaged a bypass valve to completely (or nearly so) release the pressure. Such a switch would need to be covered to prevent accidentally pushing it when a load was supported. But it would rectify my sole complaint about the ARB Jack’s operation.
Graham tries futilely to hurry the lowering process . . .
. . . while Roseann takes her time.
Some people with whom I’ve discussed the ARB Jack have brought up the inevitable argument: “Can you winch with it? Can you clamp with it?” To which I ask, how many times have you winched or clamped with a Hi-Lift jack except to try it? I can answer for myself: zero. I’d bet a lot of cash that an exceptionally tiny fraction of Hi-Lift owners have ever used theirs in anger as anything except a jack.
The rubber sleeve slides up or down to protect the vehicle's sheet metal.
Conclusions? The ARB Jack is distinctly superior at its primary function of jacking, compared with the Hi-Lift and its many copies. It’s lighter, it’s easier to handle, it takes much less effort to raise a vehicle and literally no effort to lower it, it is significantly safer (although obviously safety depends heavily on the operator for either product), and it is much easier to store.
It remains to be seen if the ARB Jack will prove as durable as the Hi-Lift, many of which have been going strong for decades. The slowness in lowering once a load is removed is annoying but definitely a first-world problem. (Still, it would be nice to see a relief valve added at some point.) I have little doubt aftermarket companies, and ARB itself, will soon fill the gap for expanded bases and other accessories.
Fine sand can collect against the piston seal. Best to keep this clean.
The sole remaining issue is that 812-pound gorilla. When I (reluctantly) turned in the jack to the ARB dealer in Perth, the manager told me they’d been selling every one they could get. So perhaps in this current overlanding world of $2,000 fridges, $4,000 roof tents, and $20,000 adventure trailers, an $800 jack is going to be no big deal. If you’re considering one, I can at least assure you that it will work as advertised—it is a very, very fine tool.
ARB Jack: $812. Leaving a stylish brand in the Australian sand: Priceless.
For want of an M8 x 30mm bolt . . .
It still amazes me how well I can prepare for a long, remote journey, yet still find myself unprepared.
Over the course of four trips to Australia in the Land Cruiser Troopy we bought there, I slowly accumulated a pretty decent selection of tools, highlighted by a superb Bahco S106 combination kit (see here), which includes full 1/4 and 1/2-inch socket sets, wrenches, plus numerous drive fittings. An additional set of 1/2-inch deep sockets, a screwdriver selection, an electrical tester, and various pliers rounds out the kit.
Our recent trip was without doubt the hardest on both our Troopy and that belonging to Graham Jackson and Connie Rodman, as we covered 2,600 kilometers of dirt tracks between Coober Pedy to Perth, some of them heavily corrugated. And as on earlier trips, substandard work done by a mechanic in Sydney (not the Expedition Centre which did all the camper conversions, but a repair shop nearby) began to manifest itself. A new radiator installed on Graham’s vehicle, bought long distance before we arrived—and guaranteed by the mechanic to be “as good as Toyota”—began leaking halfway through the journey. Radiator stop-leak controlled but did not completely plug it. Next, I found the transfer case lever in our vehicle would engage four wheel drive but flopped back and forth rather than engage low range. The nut on that section of linkage had fallen off. (The transmission had been removed to repair a leak before a previous trip.)
A bit farther on, Roseann and I started noticing a rattle that seemed to be coming from the exhaust, as if some gravel had become caught on top of a heat shield. But soon we could hear an obvious exhaust leak. Underneath the vehicle I inspected the “performance” exhaust system the mechanic had installed. A joint near the middle was completely loose. It had been connected with two bolts and nuts—no flat washers, no lock washers, no jam or nylock nut, no Loctite. One bolt and nut was completely gone; the other I easily removed with my fingers, to find most of the thread stripped.
And that was a problem, because while I had plenty of tools with which to install or remove virtually any nut or bolt on the truck, I had not gotten around to the item on my pre-trip list that read BUY SPARE BOLTS AND NUTS.
Sigh . . .
This time I got lucky. We had some leftover washers from a RAM mount, plus several bolts I had bought to secure it, and against all odds they just happened to be a suitable size and length. We were soon back on the road with a quiet exhaust (and Graham had found an extra M8 nut with which to fix the low-range linkage).
Needless to say, when we got to Perth I made my first task a trip to the local Bunnings to get a start on rectifying the situation before we loaded the Land Cruisers into a container for Africa.
One suggestion: I usually buy mostly high-tensile spare bolts (Grade 8 in SAE or 8.8 or 10.9 in metric), figuring that it won't hurt to replace a missing standard bolt with a high-tensile spare, and I can be assured of having the proper strength fastener for a critical component.
The Hiplok Z Lok
Securing one’s possessions while on a trip is an annoying but critical concern. Inside the vehicle we lock down our large, important items—Pelican cases, etc.—with bicycle-style cables and padlocks stout enough to resist all but a really determined criminal with bolt-cutters and time.
But there are many other smaller items, and other circumstances, where one needs minimal protection from a snatch-and-run thief, involving minimal hassle and weight. Some time ago I read about the Z Lok from Hiplok, and my bicycling friend Geoff in Sydney just gave me one.
The Z Lok is essentially a glorified ziptie, but much stouter, cored with a strip of steel—and, saliently, reusable. A simple forked key disengages the double steel teeth that secure the tie inside a steel-reinforced head. It’s strong enough to resist a really strong yank, and would be nearly impossible to cut with a knife (although not with a good pair of side cutters).
While any thief could buy one and carry the forked key around looking for an opportunity, that’s an unlikely scenario. The Z Lok would be excellent for many situations—locking my camera case to the table while I’m having lunch at an outdoor café; securing my bicycle helmet to the bike—even quickly locking the bike itself if I just wanted to duck inside a coffee shop for a takeaway.
At around 12 bucks on Amazon, or $20 for a pair, I can think of a zillion uses for these things.
Don't be the beta tester
Roof rack brackets broken straight through the adjustment holes
A few years ago my wife and I helped lead a self-drive trip along the U.S. portion of the Continental Divide, the great mountain range that divides North America’s watershed. In addition to our 2012 Tacoma and Four Wheel Camper and the other trip leader’s Ford Raptor, there were a dozen vehicles along, ranging from a pristine late 80s Ford Bronco to a couple of Sportsmobiles, FJ Cruisers, and Jeep Wranglers. Another Raptor and Tacoma, and a recently restored FJ60 Land Cruiser completed the convoy.
Several of the participants had done a lot of last-minute modifications to their vehicle to prepare for the trip, and the FJ60 was fresh off a major rebuild, with some untested components of its own.
It soon began to show.
Climbing through New Mexico, one of the FJ Cruisers pulled off to the side of the trail, and the owner climbed out and began inspecting the custom tire carrier on the back. We stopped and I went over, to find that welds on the carrier were beginning to split, allowing the rack and tire to bang back and forth. We used some ratchet straps to secure the carrier and belay any further cracking—which if left unchecked would have eventually allowed the entire assembly to fall off.
By the Colorado border other issues were surfacing.
A custom auxiliary battery tray on another vehicle began to rattle itself loose. A four-wheel-drive Chevy Van had developed narcolepsy, and would simply stop running for an hour or two, then magically wake up.
A rough trail over a high pass into Wyoming really started to shake things apart. The fenders on a cargo trailer towed by one of the support vehicles—which had been running an easier, parallel course to ours—simply fell off. Another auxiliary battery tray came loose, along with a shock absorber mount.
The FJ60 had a lightweight aluminum roof rack installed, mounted with an Autohome roof tent and a side awning. When the rack started making noise, we inspected it, and found one of the aluminum gutter mounts cracked almost all the way through. That was secured—more or less—with duct tape, and we continued. Then another one cracked, and another. Soon all six mounts were near failing. An inspection showed that, incredibly, the manufacturer—a well-respected South African company—had drilled three adjusting holes in each one right across the area where the most strength was needed. Failure on this part was never a possibility—it was an inevitability.
There was no way to adequately repair the mounts in the field, so at the next rendezvous with the support trucks we took off the entire rack, tent and all, and strapped it on top of the massive welded steel construction rack on the support truck. For the rest of the trip the two guys driving the Land Cruiser had a penthouse suite on an F450.
That Continental Divide trip was an extreme example, but I’ve run into this syndrome time after time after time: A vehicle owner has a much-anticipated trip coming up, and work schedules and budgets dictate a rush of last-minute modifications—many of which are not even really needed, just desired. And out in the real world of washboard trails and rocky hillclimbs it is discovered too late that some of those modifications were under-engineered. In the worst of cases the issues can spell the end of the trip; at best they delay progress and inconvenience traveling companions.
If you have a major trip planned, and a list of things you really want or need to do to your vehicle for that trip, do them enough in advance so you can thoroughly test their quality on shorter excursions. It’s much better to do without an accessory than to find out it is more of a hindrance than an asset. And don’t assume just because something is sold by a famous company that it actually has been proven by them before they sell it to you. Let them do their beta testing on someone else.
Smittybilt "Recovery Strap"
Before last year’s Overland Expo West, as we were juggling trucks and trailers and various four-wheel-drive vehicles to make sure we had all the transport and training equipment we’d need in Flagstaff, Roseann mentioned that we should have a basic recovery kit—a Microstart and a recovery strap—in every vehicle. Of course our main travel vehicles already had full kits to go with the winches on them, so I went online and found some inexpensive (Chinese-made) but brand-name “recovery straps” from Smittybilt. I tossed one in each of the spare trucks.
This morning, for the first time, I took one out of its cellophane wrapper, and was incredulous at what I found.
Nowhere on either the paper label or on the strap itself does it indicate whether this is a kinetic recovery strap or a non-kinetic tow strap. The only mention of materials is the note that it has “ballistic nylon reinforced ends,” which of course says nothing about the composition of the strap itself. Elastic nylon or non-elastic polyester? The paper label claims the two-inch-wide strap is rated to 20,000 pounds. Nowhere on the strap itself does it indicate this, or whether that rating is a working load limit or a minimum breaking strength. The sole scant indication of intended use comes all the way down the list of characteristics on the label, a line that says simply, “low stretch.” Does that mean minimal stretch, as one needs for a tow strap, or low stretch as in it will stretch if used kinetically, but not a lot?
My conclusion is that the Smittybilt “Recovery Strap” is actually a non-kinetic tow strap. But the lack of solid information, especially regarding the composition of the strap, and its advertisement as a “recovery” product, could effortlessly lead a consumer to employ this in a kinetic situation, with potentially disastrous consequences.
This is a bad, bad effort on Smittybilt’s part.
If you’re shopping for a tow strap or a recovery strap, make sure what you buy lists clearly its:
Precise intended use—towing or kinetic recovery
Materials—stretchy nylon or non-stretchy polyester
Working load limit (WLL) or minimum breaking strength (MBS)
And make sure all this information is on a durable label on the product itself.
Don't risk "Gargo damage." And note that "Strenght" could be reduced . . .
Hint: When using “Search,” if nothing comes up, reload the page, this usually works. Also, our “Comment” button is on strike thanks to Squarespace, which is proving to be difficult to use! Please email me with comments!
Overland Tech & Travel brings you in-depth overland equipment tests, reviews, news, travel tips, & stories from the best overlanding experts on the planet. Follow or subscribe (below) to keep up to date.
Have a question for Jonathan? Send him an email [click here].
SUBSCRIBE
CLICK HERE to subscribe to Jonathan’s email list; we send once or twice a month, usually Sunday morning for your weekend reading pleasure.
Overland Tech and Travel is curated by Jonathan Hanson, co-founder and former co-owner of the Overland Expo. Jonathan segued from a misspent youth almost directly into a misspent adulthood, cleverly sidestepping any chance of a normal career track or a secure retirement by becoming a freelance writer, working for Outside, National Geographic Adventure, and nearly two dozen other publications. He co-founded Overland Journal in 2007 and was its executive editor until 2011, when he left and sold his shares in the company. His travels encompass explorations on land and sea on six continents, by foot, bicycle, sea kayak, motorcycle, and four-wheel-drive vehicle. He has published a dozen books, several with his wife, Roseann Hanson, gaining several obscure non-cash awards along the way, and is the co-author of the fourth edition of Tom Sheppard's overlanding bible, the Vehicle-dependent Expedition Guide.